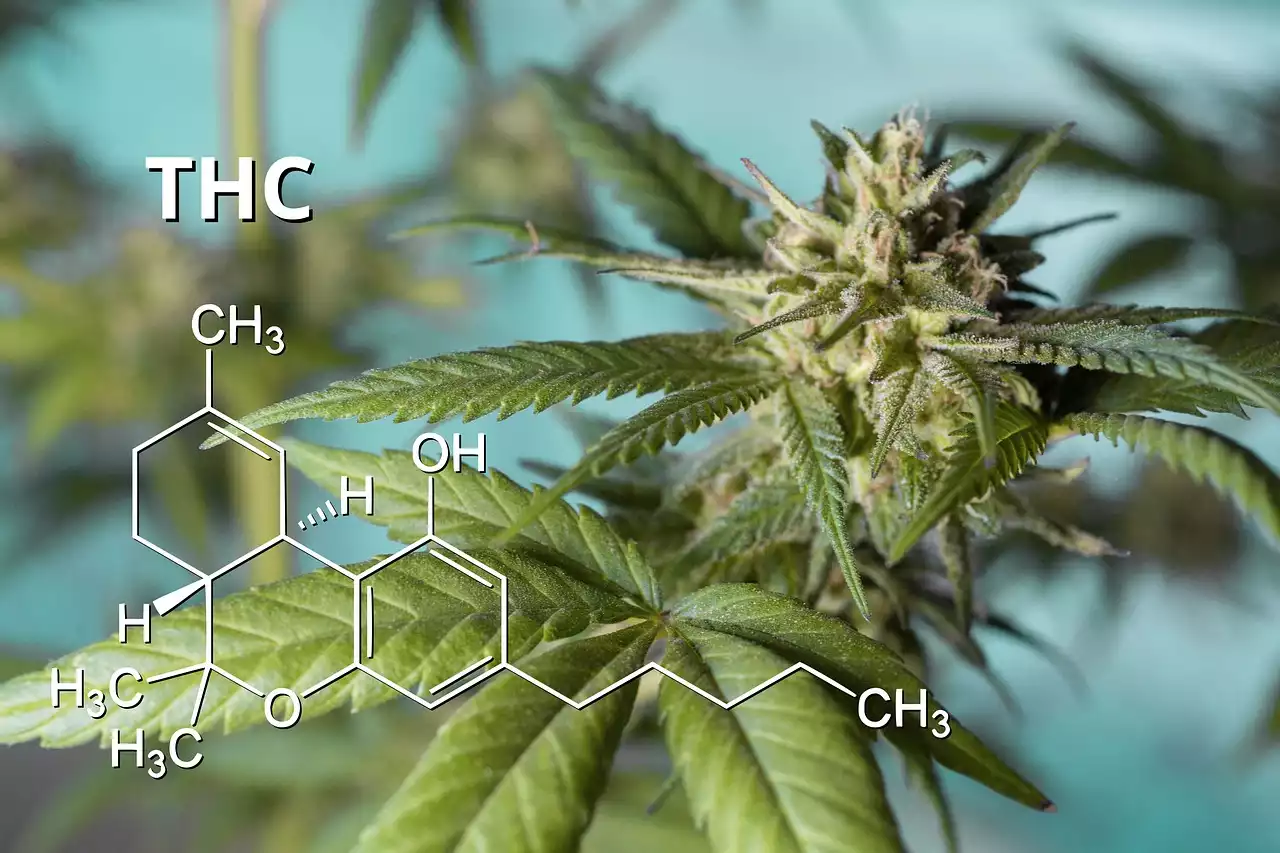
What is Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)?
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is a cannabinoid found in the cannabis plant. It is the primary psychoactive compound responsible for the "high" associated with cannabis use. THC interacts with the body's endocannabinoid system, which regulates various physiological and cognitive processes, including appetite, pain sensation, mood, and memory.
THC binds to the cannabinoid receptors in the brain and other parts of the body, triggering a series of effects that can alter mood, perception, and behavior. However, THC's effects are not limited to its psychoactive properties. Research suggests that THC has several therapeutic benefits that could make it a valuable tool in modern medicine.
The history of THC in medicinal use
Cannabis has been used for medicinal purposes for thousands of years. Ancient civilizations, such as the Egyptians, Greeks, and Chinese, used cannabis to treat various ailments, including pain, inflammation, and anxiety. However, it wasn't until the 20th century that scientists began to isolate and study the plant's active compounds, including THC.
In the 1980s, researchers discovered the endocannabinoid system, a complex network of receptors and molecules that help regulate various physiological processes. This discovery opened up new avenues for studying the therapeutic potential of cannabinoids, including THC.
Today, an increasing number of states have legalized cannabis for medical purposes, and THC is being studied for its potential to treat a range of conditions, from chronic pain to cancer.
How THC interacts with the body's endocannabinoid system
THC interacts with the body's endocannabinoid system by binding to the CB1 and CB2 receptors. CB1 receptors are primarily found in the brain and central nervous system, while CB2 receptors are found in the immune system and peripheral tissues.
When THC binds to these receptors, it can trigger various effects, including pain relief, appetite stimulation, and mood alteration. Additionally, THC can also affect the release of neurotransmitters, including dopamine and serotonin, which play a role in regulating mood and behavior.
Research suggests that THC's effects on the endocannabinoid system may make it a valuable tool in treating various conditions, from chronic pain to anxiety disorders.
The potential therapeutic benefits of THC
THC has shown promise in treating a range of conditions, including:
Chronic pain
Chronic pain is one of the most common reasons people seek medical cannabis. Studies suggest that THC may help reduce pain by activating the endocannabinoid system and blocking pain signals. Additionally, THC may also help reduce inflammation, which can contribute to chronic pain.
Appetite stimulation
THC is known for its ability to stimulate appetite, which can be beneficial for people undergoing chemotherapy or suffering from conditions that cause a loss of appetite. THC may also help regulate metabolism, which can be helpful for people with obesity or diabetes.
Anxiety and depression
While high doses of THC can trigger anxiety and paranoia, low doses may have the opposite effect. Studies suggest that THC may help reduce anxiety and depression by activating the endocannabinoid system and increasing the release of neurotransmitters, such as serotonin.
Neurodegenerative diseases
THC may also have potential in treating neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's. Studies suggest that THC may help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, which can contribute to the development of these conditions.
Research studies on the medical applications of THC
Research into the medical applications of THC is ongoing, and while there is still much to learn, there have been several promising studies in recent years.
One study published in the Journal of Pain found that cannabis containing THC was effective in reducing chronic pain in patients with neuropathic pain. Another study published in the Journal of Psychopharmacology found that low doses of THC were effective in reducing anxiety in people with social anxiety disorder.
Additionally, a study published in the Journal of Alzheimer's Disease found that THC was able to reduce inflammation and restore cognitive function in mice with Alzheimer's disease.
While these studies are promising, more research is needed to fully understand the therapeutic potential of THC and how it can be used to treat various conditions.
The legal status of THC and medical marijuana
The legal status of THC and medical marijuana varies from state to state and country to country. In the United States, 36 states have legalized medical marijuana, with varying restrictions on THC content and consumption methods.
While medical marijuana is legal in many states, it is still classified as a Schedule I drug at the federal level, which means that it is considered to have no medicinal value and a high potential for abuse. This classification has made it difficult for researchers to study the therapeutic potential of THC and other cannabinoids.
However, as more states legalize medical marijuana and the public perception of cannabis shifts, there is hope that THC and other cannabinoids will be reclassified and more research will be allowed.
Different methods of consuming THC for therapeutic purposes
There are several different methods of consuming THC for therapeutic purposes, including:
Smoking or vaping
Smoking or vaping cannabis is one of the most common ways to consume THC. When cannabis is smoked or vaporized, THC is rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream, producing a quick onset of effects.
Edibles
Edibles, such as brownies or gummies, are another popular way to consume THC. When THC is consumed in an edible form, it is metabolized by the liver, producing a slower onset of effects that can last for several hours.
Tinctures and oils
Tinctures and oils are concentrated forms of THC that can be taken orally or sublingually. When taken sublingually, THC is absorbed through the mucous membranes in the mouth, producing a quick onset of effects.
Topicals
THC-infused topicals, such as creams or balms, can be applied directly to the skin to provide localized pain relief without producing psychoactive effects.
It's important to note that different methods of consuming THC can produce different effects and have varying onset times. Additionally, dosing can be difficult, and it's important to start with a low dose and titrate up slowly to avoid unwanted side effects.
Potential side effects and risks of THC use
While THC has several potential therapeutic benefits, it also carries some risks and side effects. Some of the most common side effects of THC use include:
Dry mouth
THC can cause a dry mouth, which can be uncomfortable but is usually not serious.
Increased heart rate
THC can increase heart rate, which can be problematic for people with heart conditions.
Impaired memory and concentration
High doses of THC can impair memory and concentration, which can be problematic for people who need to perform complex tasks.
Additionally, THC can also cause paranoia, anxiety, and psychotic symptoms in some people, particularly at high doses.
The future of THC in medical treatments
As more research is conducted on the therapeutic potential of THC, it's possible that we will see more widespread use of this compound in modern medicine. However, there are still many obstacles to overcome, including legal restrictions and limited research funding.
Additionally, more research is needed to fully understand the therapeutic potential of THC and how it can be used to treat various conditions. By gaining a better understanding of how THC works and its potential benefits, we can unlock new possibilities for alternative treatments and improve the lives of millions of people.
Conclusion: The importance of further research and understanding THC's therapeutic potential
THC has several potential therapeutic benefits that go beyond its psychoactive effects. From pain management to appetite stimulation and reducing anxiety, THC has shown promise in treating a range of conditions.
While more research is needed to fully understand THC's therapeutic potential and how it can be used to treat various conditions, the future looks promising. As more states legalize medical marijuana and the public perception of cannabis shifts, there is hope that THC and other cannabinoids will be reclassified and more research will be allowed.
By gaining a better understanding of how THC works and its potential benefits, we can unlock new possibilities for alternative treatments and improve the lives of millions of people. Let's continue to explore the exciting possibilities that lie beyond the high and shed light on THC's promising future in modern medicine.